Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is a widely recognized 3D printing technology that has revolutionized the manufacturing landscape. This method, often referred to as fused deposition modeling services, utilizes thermoplastic materials to create three-dimensional objects layer by layer. But how exactly does this process work, and what are its practical applications across various industries?
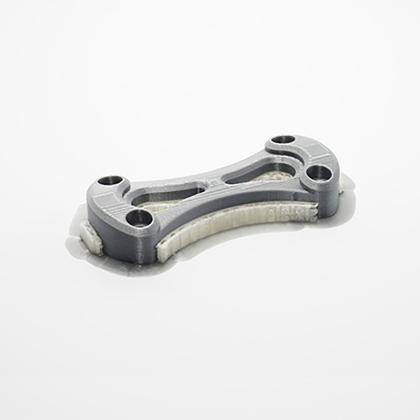

How Fused Deposition Modeling Works
The core principle of FDM involves the extrusion of heated thermoplastic filament through a nozzle. The process can be broken down into several key steps:
- Material Selection: Various thermoplastics, such as ABS, PLA, and PETG, can be used depending on the desired properties of the final product.
- Design Creation: A 3D model is designed using CAD software, which is then sliced into layers using slicing software.
- Printing Process: The printer heats the filament and extrudes it onto a build platform, where it cools and solidifies, forming the object layer by layer.
- Post-Processing: Once printing is complete, the object may require additional finishing processes, such as sanding or painting, to achieve the desired appearance.
Applications of Fused Deposition Modeling Services
The versatility of fused deposition modeling services allows for a wide range of applications across multiple sectors:
- Prototyping: FDM is extensively used for rapid prototyping, enabling designers to create functional prototypes quickly and cost-effectively.
- Aerospace: The aerospace industry utilizes FDM for producing lightweight components that meet stringent safety and performance standards.
- Healthcare: Customized medical devices and anatomical models are created using FDM, enhancing surgical planning and patient-specific treatments.
- Automotive: In the automotive sector, FDM is employed for producing complex parts and tooling, reducing lead times significantly.
Benefits of Fused Deposition Modeling Services
Why should businesses consider adopting fused deposition modeling services? Here are some compelling advantages:
- Cost-Effectiveness: FDM is generally more affordable than other 3D printing methods, making it accessible for small and medium-sized enterprises.
- Material Variety: A wide range of thermoplastic materials can be used, allowing for tailored properties based on specific application needs.
- Ease of Use: FDM printers are user-friendly and require minimal training, making them suitable for various skill levels.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fused deposition modeling services represent a significant advancement in the field of 3D printing. By understanding how FDM works and its diverse applications, businesses can leverage this technology to enhance their production capabilities. For more information on FDM services, consider exploring  .
.