Unlocking the Magic of PLA: Discover the Secrets Behind Its 3D Printing Power!
In the rapidly evolving world of 3D printing, one material has emerged as a favorite among enthusiasts and professionals alike: PLA filament. Short for Polylactic Acid, PLA has gained popularity due to its versatility and user-friendly properties. As 3D printing technology becomes more accessible, understanding the materials we use is crucial. PLA filament stands out not just for its ease of use, but also for its environmental benefits and wide range of applications. In this article, we will delve into the properties that make PLA unique, explore the benefits of using it in 3D printing, and examine its diverse applications across various fields.
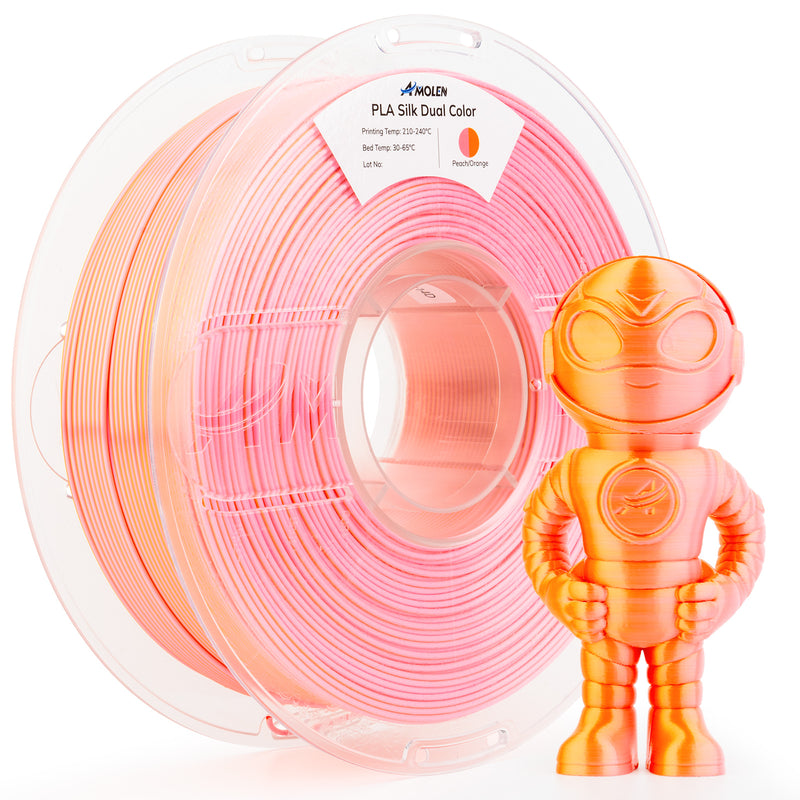

Understanding PLA Filament Properties
PLA filament is derived from renewable resources, primarily corn starch or sugarcane, which gives it a unique edge over petroleum-based filaments. Its chemical composition leads to several physical characteristics that define its performance. PLA typically has a melting temperature ranging from 150°C to 160°C, making it relatively easy to print compared to other materials like ABS. With a density of around 1.24 g/cm³, PLA is lightweight yet offers a commendable tensile strength, allowing for the production of durable prints. While PLA is generally stiffer than some other filaments, its brittleness can be a consideration in applications requiring flexibility. Compared to ABS, which is known for its heat resistance and durability, PLA tends to be less resilient but compensates with its ease of use and lower warping tendencies, making it an ideal choice for beginners.
Benefits of Using PLA Filament in 3D Printing
The advantages of PLA filament extend beyond its composition. One of the standout benefits is its biodegradability—an appealing feature for environmentally-conscious users. Unlike many other filaments that can linger in landfills for centuries, PLA can decompose under the right conditions, making it a more sustainable choice. Additionally, PLA is known for its low warping properties, which simplifies the printing process. This characteristic is particularly beneficial for beginners who may struggle with more temperamental materials. With a wide printing temperature range and compatibility with most 3D printers, PLA is user-friendly, allowing both novices and experienced users to achieve great results. It's also available in a multitude of colors and finishes, providing endless creative possibilities. A friend of mine, an avid 3D printing hobbyist, often emphasizes how PLA has transformed his projects, allowing him to experiment without the fear of failed prints.
Applications of PLA Filament
The versatility of PLA filament is evident in its broad range of applications. In the world of prototyping, PLA is frequently used for creating functional models, thanks to its ability to produce detailed and accurate representations. In educational settings, teachers and students leverage PLA to bring concepts to life through hands-on projects. For instance, a local school recently utilized PLA to print anatomical models for biology classes, enhancing student engagement and understanding. Moreover, artists and designers are increasingly turning to PLA for their creative endeavors, crafting intricate sculptures and decorative items. The ease of post-processing with PLA, such as sanding and painting, further extends its usability in artistic applications. The adaptability of PLA makes it a go-to filament across industries, proving its worth in various contexts.
Best Practices for Printing with PLA Filament
To achieve optimal results when printing with PLA, it is essential to maintain several best practices. First, set your 3D printer's extruder temperature between 180°C to 220°C and the bed temperature around 60°C. This helps improve adhesion and prevents warping. It's also crucial to keep PLA dry, as moisture absorption can negatively impact print quality. Using painter's tape or glue on the printer's bed can further enhance stickiness, ensuring your print stays in place. Finally, avoid cooling down too quickly after printing to reduce stress and cracking. Following these guidelines will help users achieve high-quality results with their PLA prints.
Summary of PLA Filament Benefits and Applications
In summary, PLA filament is a remarkable material that has significantly impacted the 3D printing landscape. Its unique properties, such as biodegradability, low warping, and ease of use, make it an ideal choice for a wide range of applications, from prototyping to education and artistic endeavors. As we continue to explore the potential of 3D printing technology, PLA stands out as a material that not only supports creativity and innovation but also promotes sustainability. For anyone looking to dive into the world of 3D printing or expand their material repertoire, PLA filament is undoubtedly worth considering for your next project.