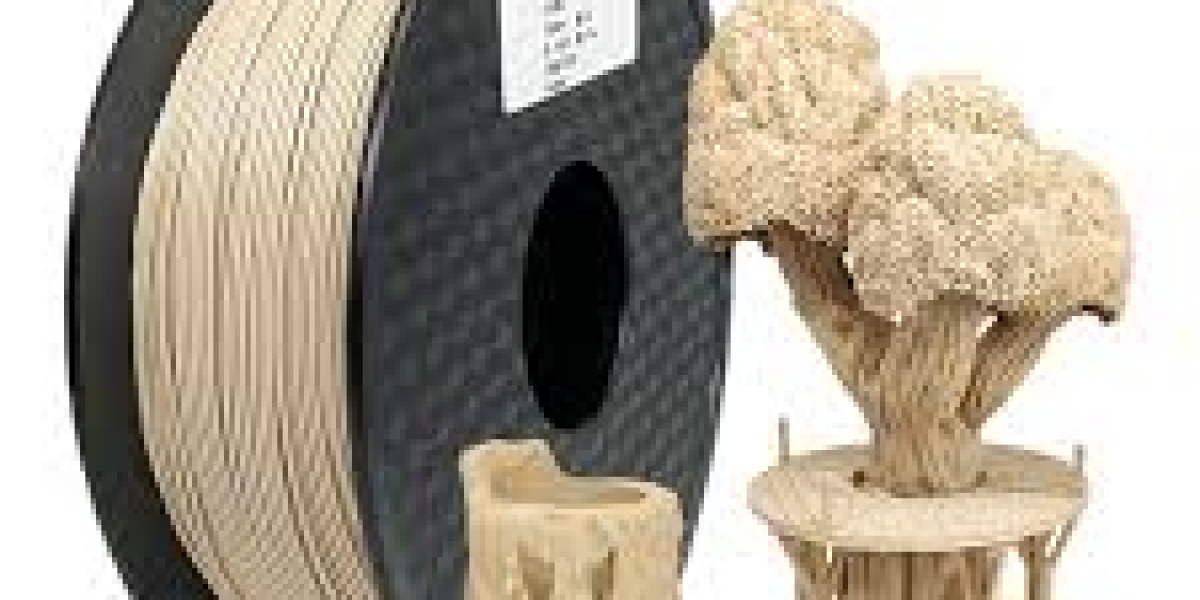
However, to achieve consistent quality and extend the filament’s usable life, it’s essential to store and handle wood filament under specific environmental conditions. As wood filament can be sensitive to moisture and temperature changes, maintaining the right conditions ensures high-quality prints and minimizes material waste.
Humidity Control for Moisture Resistance
Wood filament is highly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the air. If the filament absorbs too much moisture, it can lead to issues like stringing, poor layer adhesion, and even bubbling during extrusion, compromising print quality. To prevent this, it’s crucial to store wood filament in a low-humidity environment. Ideally, keep the relative humidity below 20-30%. Using airtight storage containers with desiccants or silica gel packs is a practical way to control moisture, ensuring the filament remains dry and ready to use.
Temperature Stability
Temperature fluctuations can affect the integrity and print performance of wood filament. High temperatures may cause filament warping or melting, while extreme cold can make it brittle, increasing the likelihood of breakage during printing. To avoid these issues, store wood filament in a cool, stable environment, ideally between 15-25°C (59-77°F). Avoid areas like garages, basements, or outdoor sheds, where temperatures can vary significantly throughout the day. A controlled indoor environment provides the best protection against temperature-induced degradation.
Protection from Light and UV Exposure
UV light exposure can degrade both the wood particles and PLA in the filament, leading to color changes and brittleness over time. Storing wood filament away from direct sunlight or artificial UV light sources helps preserve its natural appearance and structural integrity. Opaque storage containers or UV-resistant bags are ideal for protecting filament from light exposure, ensuring it retains its quality and wood-like texture for longer periods.
Proper Handling to Prevent Breakage
Wood filament can be slightly more brittle than standard PLA, especially if it’s exposed to adverse environmental conditions. To avoid filament breakage, handle spools carefully and avoid bending or stretching the filament too tightly. When setting up for a print, keep filament paths smooth and reduce tension to prevent snapping. Storing wood filament spools vertically also reduces unnecessary stress on the filament, ensuring smooth feeding during the print process.
In summary, storing wood filament under the right environmental conditions—controlling humidity, stabilizing temperature, minimizing UV exposure, and careful handling—are essential for maintaining filament quality. By following these guidelines, 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals can enjoy high-quality prints with a unique, natural wood aesthetic, while reducing the risk of wasted material due to environmental degradation.