Unlock the Secrets of PETG Filament: Why Every 3D Printer Enthusiast Needs to Know!
In the realm of 3D printing, the materials we choose play a crucial role in the quality and usability of our prints. One material that has been gaining significant traction in the 3D printing community is PETG filament. Known for its unique combination of strength, flexibility, and ease of use, PETG is rapidly becoming a favorite among hobbyists and professionals alike. Understanding PETG's properties and benefits is essential for any enthusiast looking to enhance their 3D printing experience. This article will delve into the world of PETG filament, detailing its composition, characteristics, and practical applications, ensuring you're well-equipped to take on your next project with confidence.
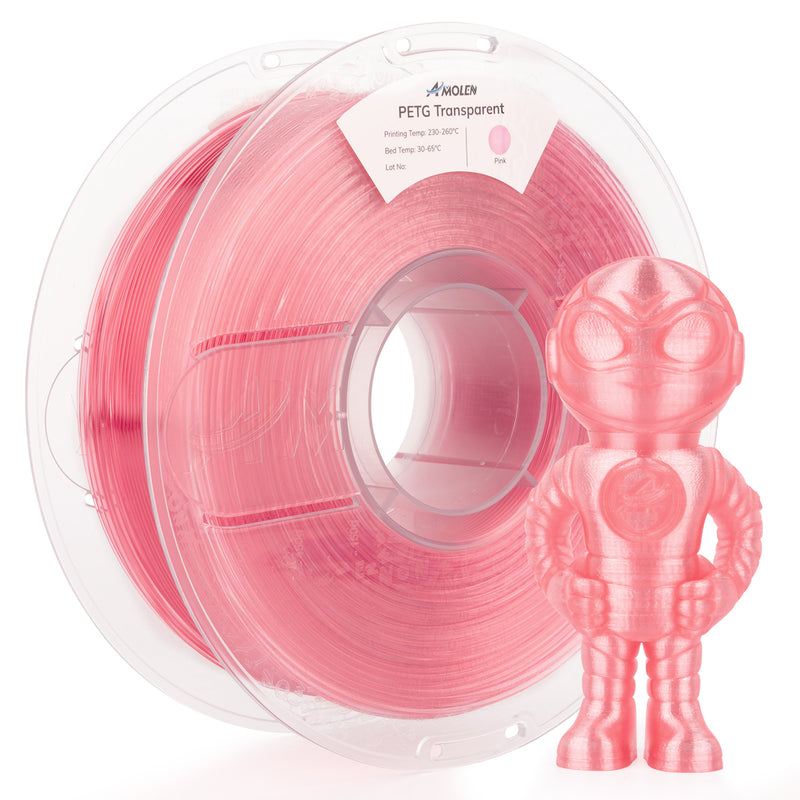

1. What is PETG Filament?
PETG, or Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol, is a thermoplastic copolyester that is widely used in 3D printing. Unlike other popular filaments such as PLA (Polylactic Acid) and ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene), PETG is known for its durability and resistance to impact. The addition of glycol during the manufacturing process results in a filament that boasts enhanced clarity and reduced brittleness compared to regular PET. This unique formulation makes PETG a versatile material that bridges the gap between the ease of PLA and the robustness of ABS. Its chemical structure allows for easy processing and excellent layer adhesion, making it an attractive choice for both beginners and experienced users.
2. Properties of PETG Filament
PETG filament is celebrated for its impressive properties that cater to a wide range of 3D printing applications. One of its standout features is its strength; PETG is significantly tougher than PLA, making it ideal for functional parts that require durability. Additionally, it offers a degree of flexibility, allowing it to withstand bending and twisting without breaking. Temperature resistance is another key property, as PETG can endure higher temperatures than PLA, making it suitable for items exposed to heat. Moreover, PETG exhibits good chemical resistance, which means it can handle various substances without degrading. These characteristics make PETG a preferred choice for projects that demand a balance of strength and resilience.
3. Benefits of Using PETG in 3D Printing
The advantages of using PETG filament in 3D printing are manifold. One of the primary benefits is the ease of printing; PETG typically requires lower printing temperatures than ABS, making it more accessible for beginners. Additionally, PETG has excellent adhesion properties, reducing the risk of warping and ensuring that prints adhere well to the build plate. This filament also produces high-quality prints with a glossy finish, enhancing the aesthetic appeal of the final product. Compared to other filaments, PETG strikes a fine balance between performance and usability, making it an excellent choice for a variety of applications. Many users, including a friend of mine who recently delved into 3D printing, have found PETG to provide a perfect mix of durability and ease, leading to successful projects with minimal hassle.
4. Use Cases of PETG Filament
PETG filament's versatility shines through in its wide array of use cases. From prototyping to functional parts, PETG is suitable for a variety of applications. For instance, it is commonly used in the production of prototypes due to its strength and detail retention, allowing designers to test their concepts effectively. Additionally, PETG is ideal for creating parts that need to withstand wear and tear, such as brackets, clips, and other functional components. The material is also popular in consumer products, ranging from household items to custom accessories. Industries such as automotive and medical have begun to harness the benefits of PETG for producing durable yet lightweight components. Given its robust characteristics, it has become a go-to material for many creators looking to produce high-quality, functional items.
5. Tips for Working with PETG Filament
When working with PETG filament, several best practices can help ensure successful prints. First, it’s crucial to set the right temperature; typically, PETG prints best at nozzle temperatures between 220°C to 250°C. Additionally, bed adhesion can be enhanced by using a heated bed set at around 70°C, which helps prevent warping during the printing process. Another tip is to use a glue stick or painter's tape on the build plate, as this can further improve adhesion. One common challenge users face with PETG is stringing, which can be mitigated by adjusting retraction settings and reducing print speed. Post-processing options, such as sanding or dyeing, can also be employed to achieve the desired finish. By keeping these tips in mind, users can navigate common challenges and maximize the potential of PETG filament.
Maximizing Your 3D Printing Experience with PETG
In conclusion, PETG filament stands out as a remarkable material in the world of 3D printing, thanks to its unique properties and versatile applications. Understanding what PETG is and how it compares to other filaments can greatly enhance your printing experience. From its strength and flexibility to its ease of use and aesthetic appeal, PETG offers significant advantages that make it an excellent choice for various projects. Whether you are a seasoned printer or a newcomer, exploring the potential of PETG can lead to impressive results in your 3D printing endeavors. So, why not give PETG a try for your next project? You may find it becomes your new favorite filament!